About the structure and biological function of PG
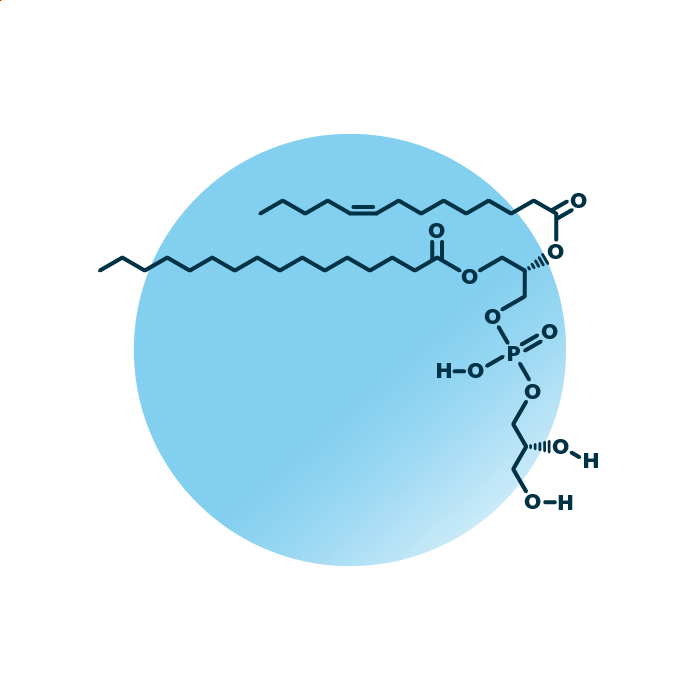
Structure. Phosphatidylglycerols (PtdGro, GPGro, or PG) belong to the group of ester phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to two fatty acids and a phosphoglycerol molecule. The fatty acids can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Phosphatidylglycerols are key intermediates in the biosynthesis of many lipids but especially of cardiolipin. They are essential for the development of normal membranes of chloroplasts and mitochondria in higher plants. In bacteria, phosphatidylglycerols are important for optimal functioning of the bacterial machinery and play a role in protein folding and binding. Further, phosphatidylglycerols have a role in the regulation of the innate immune response in the lungs.