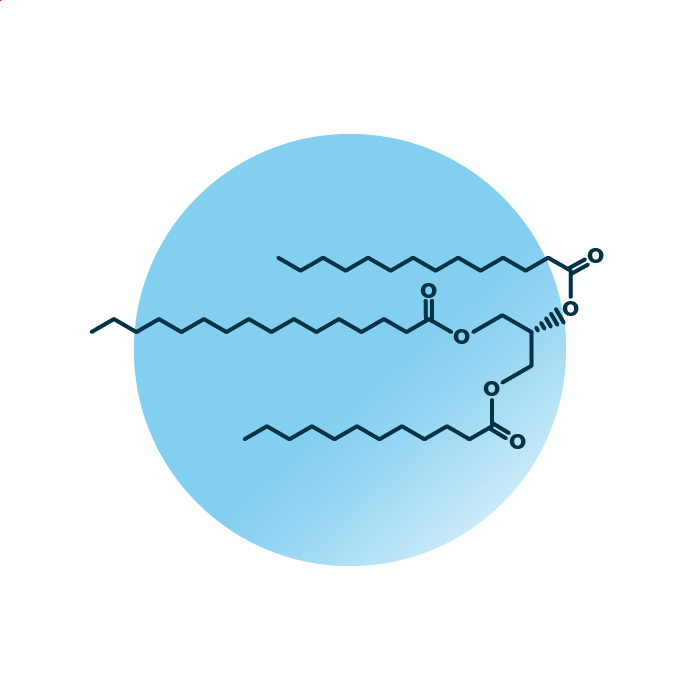
About the structure and biological function of TAG
Structure. Triacylglycerols (triglycerides, TAG, or TG) belong to the group of glycerol esters within the glycerolipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to three fatty acids. The fatty acids can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Triacylglycerols are a great source of energy in eukaryotes. Commercially important fats and oils of animal and plant origin consist almost exclusively of triacylglycerols. They also serve as pool for structural and bioactive fatty acids. The excessive accumulation of triacylglycerols in adipose tissue and other organs results in obesity and other health problems such as cardiovascular disease, fatty liver, and diabetes.