About the structure and biological function of LPS
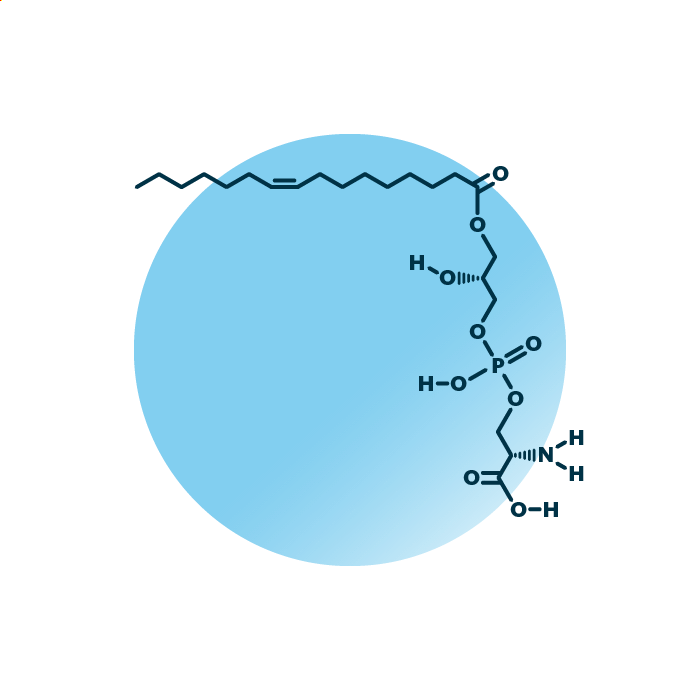
Structure. Lyso-phosphatidyl-serines (LysoPtdSer, LysoPS, or LPS) belong to the group of ester phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to a fatty acid and a phosphoserine molecule. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Lyso-phosphatidyl-serines are mediators in many biological processes, especially those of the immune system of animals. LPS levels are elevated by various inflammatory stimuli and after injury, where it can transmit the information to other cells. Thus they contribute to the resolution of inflammation. Yet, certain LPS lipids have pro-inflammatory reactions. Further, LPS metabolism aberrations are linked to cancers, night blindness, and PHARC, a genetic neurological disorder.