About the structure and biological function of LPC O-
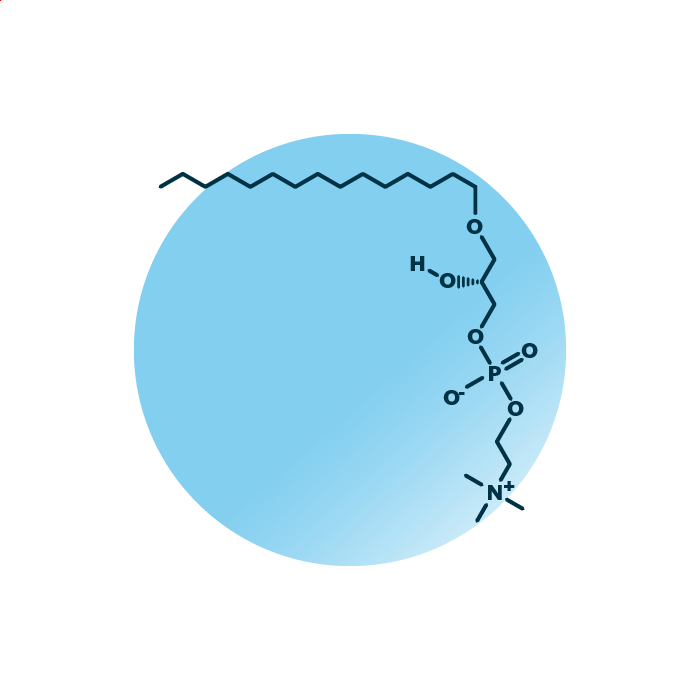
Structure. Ether-linked lyso-phosphatidyl-cholines (lysoPAF, or LPC O-) belong to the group of ether phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to a fatty alcohol via an ether bond and a phosphocholine molecule. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Little is known about the biological function of ether-linked lyso-phosphatidyl-cholines. They are precursors to ether-linked phosphatidylcholines and to platelet activating factor (PAF), which is important for inflammatory reactions but also structure and function of the central nervous system. Elevated levels of LPC O- lipids have been found in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.