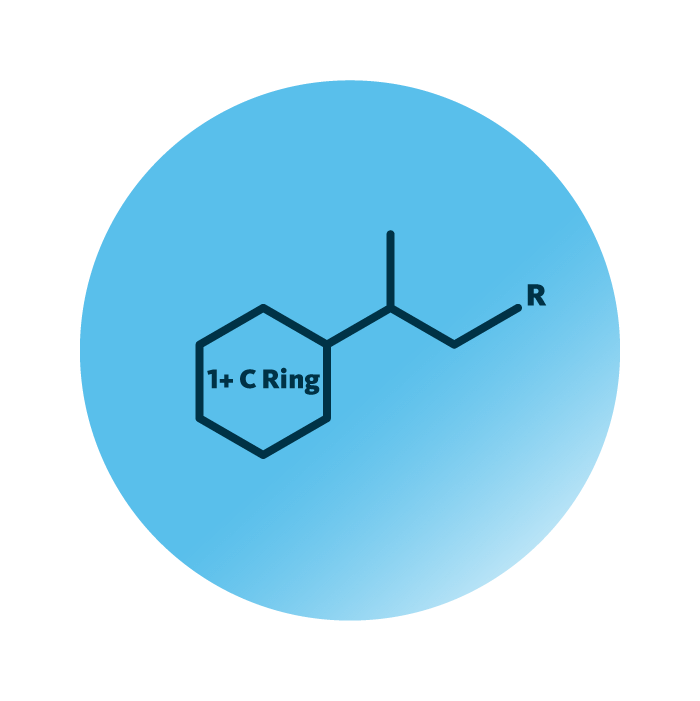
Structure. The quinones group belongs to the prenol lipids category. Their structure consists of a single- or multi-ring structure linked to a single or multiple chains made of five-carbon isoprene units, the building blocks of prenol lipids. Both, the ring structures and the isoprene chains, may encompass hydrocarbon and oxygen containing substituents, such as hydroxyl or carboxyl groups.
Function. Quinones are found in all living organisms and fulfill essential biological functions. Ubiquinones are found in membranes where they act as electron carriers between membrane-bound proteins within the electron transport chains of various processes to synthesize ATP, cellular energy. Ubiquinones also possess antioxidant properties which help protect against oxidative damage.
Tocopherols, such as vitamin E, are contributing to the formation of a complex protective network of antioxidants in plants and are essential to many aspects of animal development. Vitamin E deficiency can lead to a spectrum of neurological issues, such as speech difficulty, difficulty in coordinating movements, and other conditions. Phylloquinones, such as the vitamin K series, serve a similar function as ubiquinones but are also important to blood clotting and bone remodeling in animals.