About the structure and biological function of PA
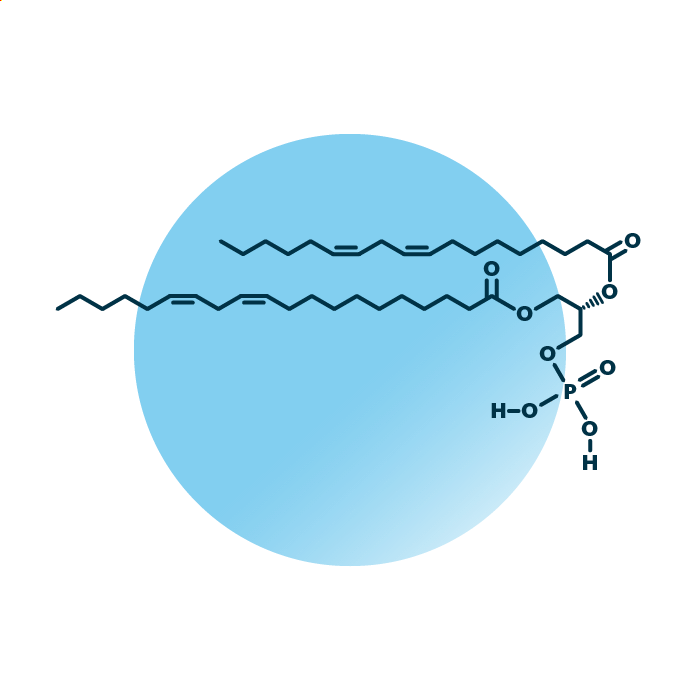
Structure. Phosphatidates (phosphatidic acids, PtdOH, or PA) belong to the group of ester phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to two fatty acids and a phosphate group. The fatty acids can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Phosphatidates are key intermediates in the synthesis of other glycerophospholipids and triacylglycerols. Yet, phosphatidates modulate signaling and cellular processes such as vesicular trafficking, enzyme activity, as well as membrane structure and dynamics. They are activators of lipid-gated ion channels. They are also precursors of lyso-phosphatidates, which are key signaling molecules. Further, the reaction product of phosphatidates with ethanol is used as biomarker for alcohol consumption and they are the key plant lipid second messengers.