About the structure and biological function of Lath
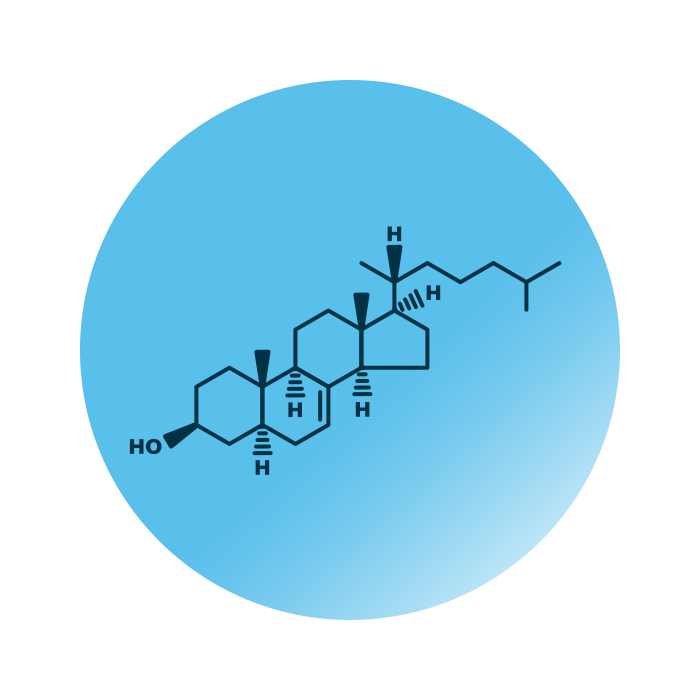
Structure. Lathosterol (cholest-7-en-3β-ol, or Lath) belongs to the group of cholesterol lipids within the sterol lipids category. Its structure consists of the steroid structure, four linked hydrocarbon rings, to which a hydrocarbon tail is linked at one end of the steroid structure and a hydroxyl group is linked to the other end. Lathosterol differs from cholesterol by the position of a double bond in the steroid structure.
Function. Lathosterol plays a significant role in the cholesterol biosynthesis serving as a cholesterol precursor in Kandutsch-Russell pathway. In human serum samples, lath levels correlate with cholesterol levels and may thus serve as biomarkers for the success of statin therapy. Further, alterations in lathosterol levels have been observed in Huntington’s disease, several types of leukodystrophy, and lathosterolosis.