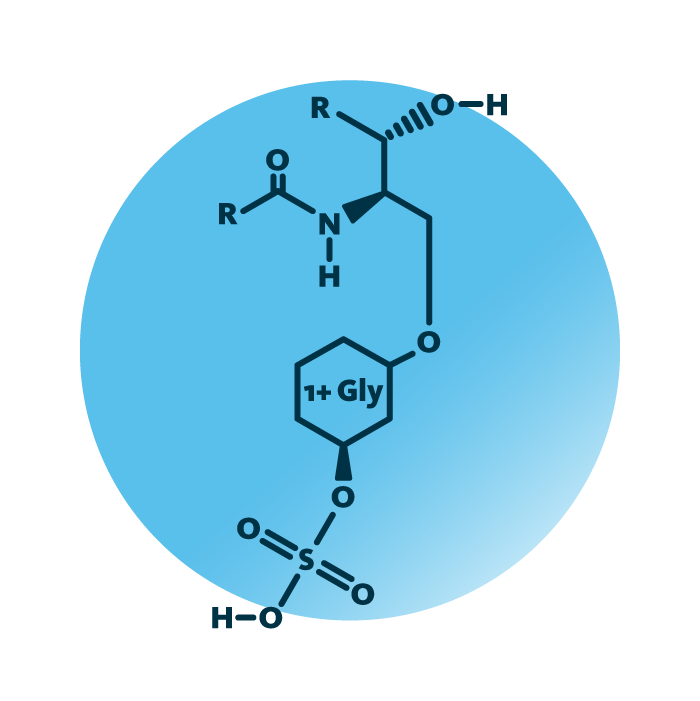
Structure. Sulfoglycosphingolipids (or glycosphingolipid sulfates) belong to the sphingolipids. Their structure consists of a ceramide backbone linked to a sulfated saccharide “head” group, such as a sulfated mono-, di-, or oligosaccharide. The ceramide backbone of sulfoglycosphingolipids contains a hydrocarbon chain termed long-chain base; one fatty acid is linked to the ceramide.
Function. Sulfoglycosphingolipids may primarily be found in animals and are involved in a plentitude of cellular processes. Many of these are consequences of sulfoglycosphingolipids binding to specific proteins and thus contributing to, for example, platelet aggregation, folding of proinsulin, and inflammation initiation.
Sulfogalactosylceramides (Sulf) are the most prominent sulfoglycosphingolipids. They are an important structural and functional constituent of myelin, the insulating layer that wraps around nerves. Many further types of sulfoglycosphingolipids, such as sulfolactosylceramides, have been discovered primarily in animal tissues, where they serve specific regional functions.