About the structure and biological function of LPA
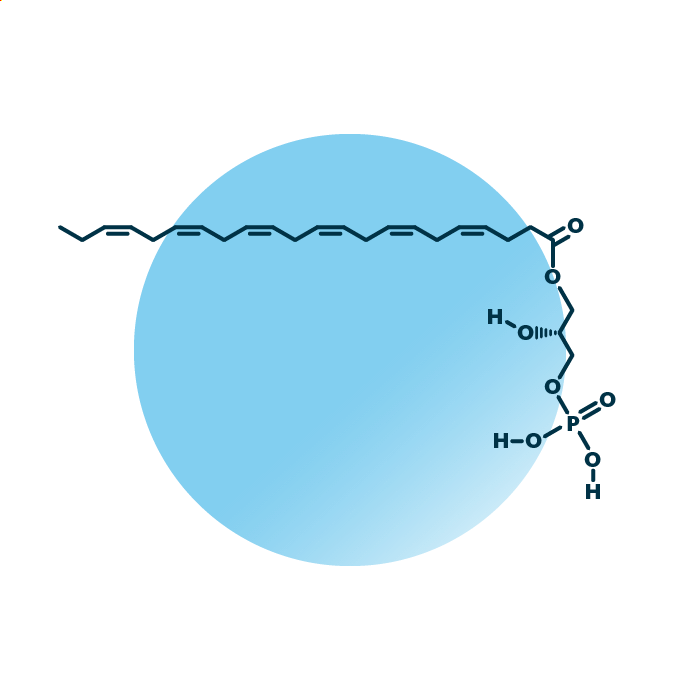
Structure. Lyso-phosphatidates (lyso-phosphatidic acids, LysoPtdOH, LysoPA, or LPA) belong to the group of ester phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to a fatty acid and a phosphate group. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Lyso-phosphatidates influence many biochemical processes in cells and act as lipid mediators with growth factor-like activities. They act upon nearly all cell types, often as signal for proliferation, cytoskeleton re-arrangement, cell differentiation, cytokine secretion, and many other vital cellular processes. Further, there is evidence for the role of LPA lipids in the remodeling of lipid metabolism in cancer. They are a target of pharmaceutical research in the search for new cancer drugs.