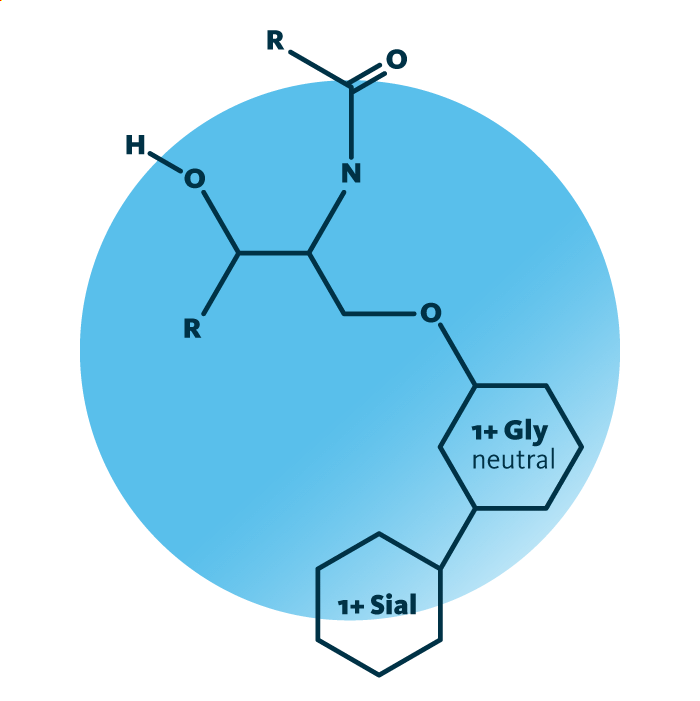
Structure. Gangliosides belong to the sphingolipids. Their structure consists of a ceramide backbone linked to an acidic oligosaccharide “head” group. The head group contains sialic acid sugars, their number is reflected in the name of ganglioside lipid classes: e.g. GT contains three sialic acids. The ceramide backbone of gangliosides contains a hydrocarbon chain termed long-chain base; one fatty acid is linked to the ceramide.
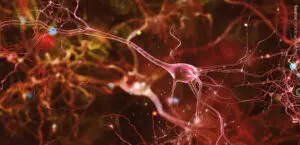
Function. Gangliosides are common to all animals but neither plants nor fungi. Their among lipids extraordinary physical properties make them essential components of cell membranes, where they support the formation of lipid rafts and caveolae, subdomains of the plasma membrane. Gangliosides are crucial in neuronal function and brain development, and can amount to 6% of the weight of lipids from the brain.
Monosialogangliosides (GM) are the most prominent gangliosides and influence neuronal functions through interaction with membrane receptors. Among the trisialogangliosides (GT), the GT1 gangliosides bind to myelin, the insulating layer that wraps around nerves, and thus connects it with the neuron. The GD3 gangliosides belong to the disialogangliosides (GD) and are critical to apoptosis, programmed cell death. Generally, ganglioside accumulation is linked to devastating diseases.