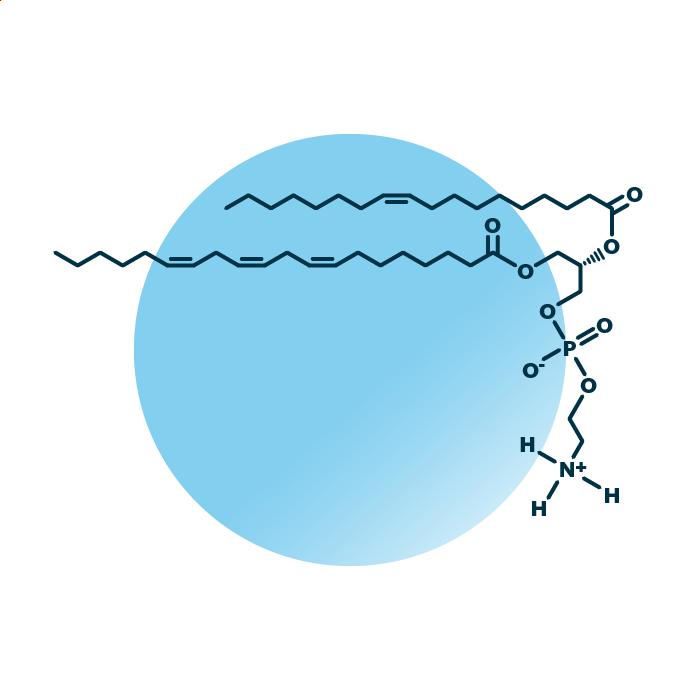
About the structure and biological function of PE
Structure. Phosphatidylethanolamines (cephalins, PtdEtn, GPEtn, or PE) belong to the group of ester phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to two fatty acids and a phosphoethanolamine molecule. The fatty acids can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Phosphatidylethanolamines serve as key building blocks for biological membranes. They are vital for mitochondria functionality where they are synthesized from phosphatidylserine. Phosphatidylethanolamines interact with a wide range of proteins, thus influencing biological processes such as neuronal development or signaling pathways. Further, phosphatidylethanolamines are linked to plant embryo viability and plant pathogen resistance.