About the structure and biological function of CE
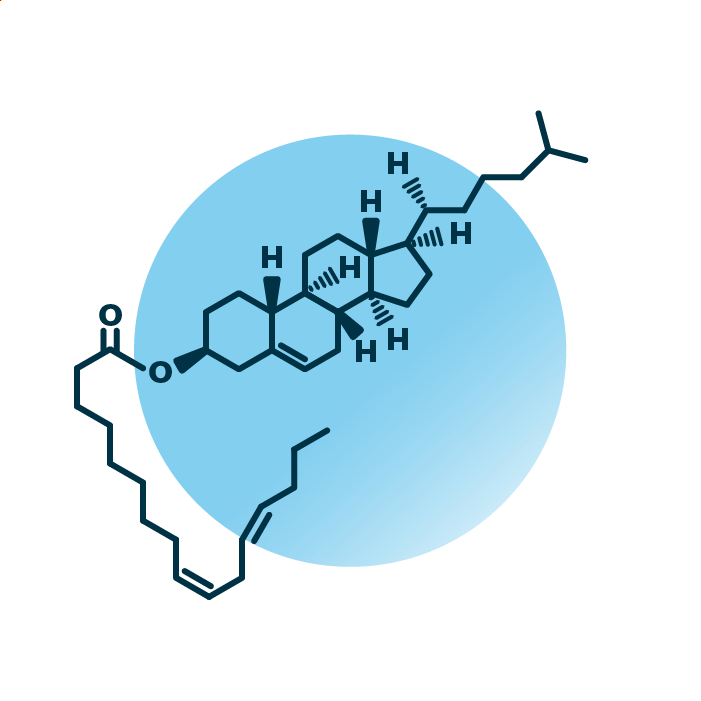
Structure. Cholesteryl esters (cholesterol esters, or CE) belong to the group of cholesterol lipids within the sterol lipids. Their structure consists of cholesterol where an ester bond is formed between the hydroxyl group of the steroid structure and a fatty acid. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Cholesteryl esters function as a transport form of cholesterol in blood plasma and in cells in lipid droplets. They serve as storage containers to buffer excess cholesterol. They also serve as pool for cholesterol, for example for hormone synthesis in the adrenal glands, but also for free fatty acids. Cholesteryl esters accumulate in fatty lesions of atherosclerotic plaques. Further, cholesterol is inefficiently converted to cholesteryl esters in the blood of cardiovascular disease patients.