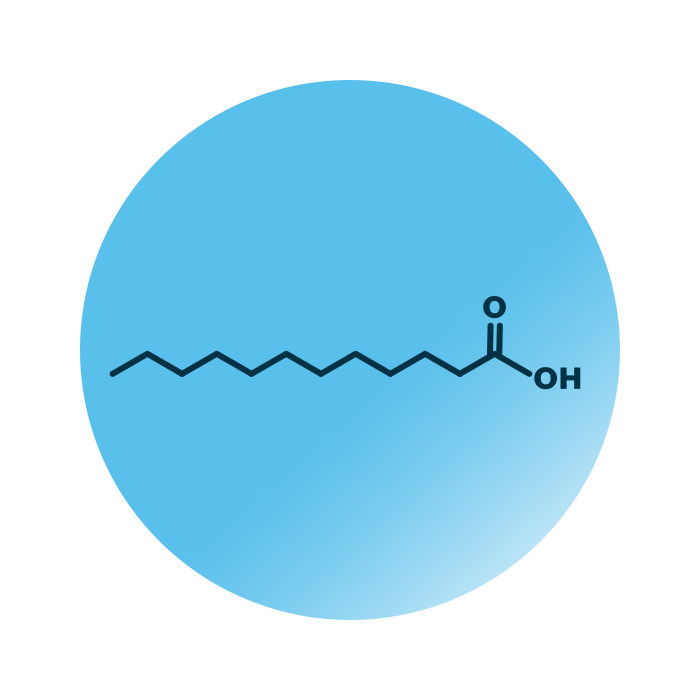
About the structure and biological function of MCFA
Structure. Medium chain fatty acids (MCFA) belong to the group of fatty acids within the fatty acyls. Their structure consists of a hydrocarbon chain of six to twelve carbon atoms and a carboxylic head group. The hydrocarbon chain of MCFAs rarely contains double bonds, yet they can be branched or linear.
Function. The biological role of medium chain fatty acids is mostly associated with energy metabolism. Many MCFAs can be found in milk fats, and are enriched in some selected seed oils. Medium chain fatty acids are rarely found in membrane lipids. The hormone ghrelin, which has been coined “hunger hormone” for its role in food intake, contains an MCFA, and some MCFAs have signaling functions. MCFAs are quickly oxidized by the liver.