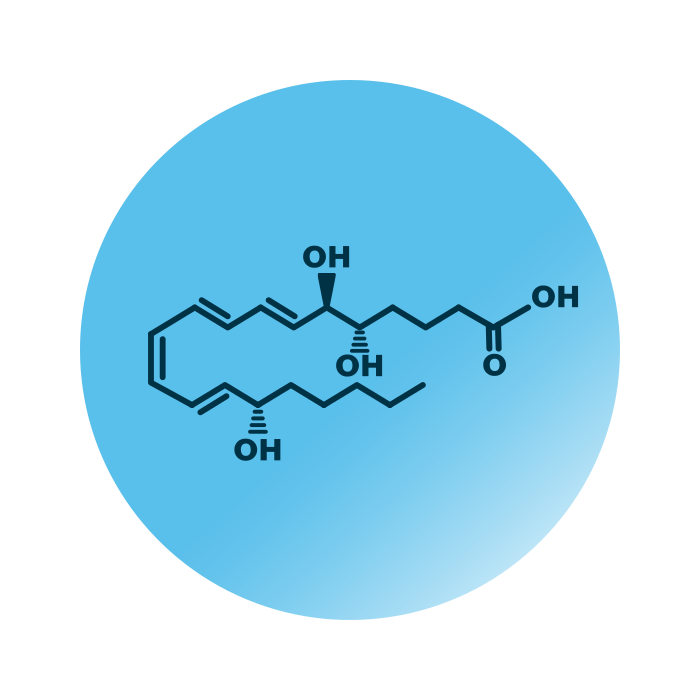
About the structure and biological function of LX
Structure. Lipoxins (LX) belong to the group of eicosanoids within the fatty acyls. Their structure is based on eicosanoic acid, a twenty carbon atoms long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group. The chain contains four double bonds in conjugation, and further features three hydroxy groups.
Function. The biological role of lipoxins mainly revolves around the resolution of inflammation. They interact with specific cell membrane embedded G-protein-linked receptors to activate signal transduction pathways in the cell. For example, LXs control the entry of neutrophils to sites on inflammation, an essential cell type of the innate immune system which is prone to causing collateral damage during prolonged activity. Further, dysregulated lipoxin function is linked to Alzheimer’s disease.