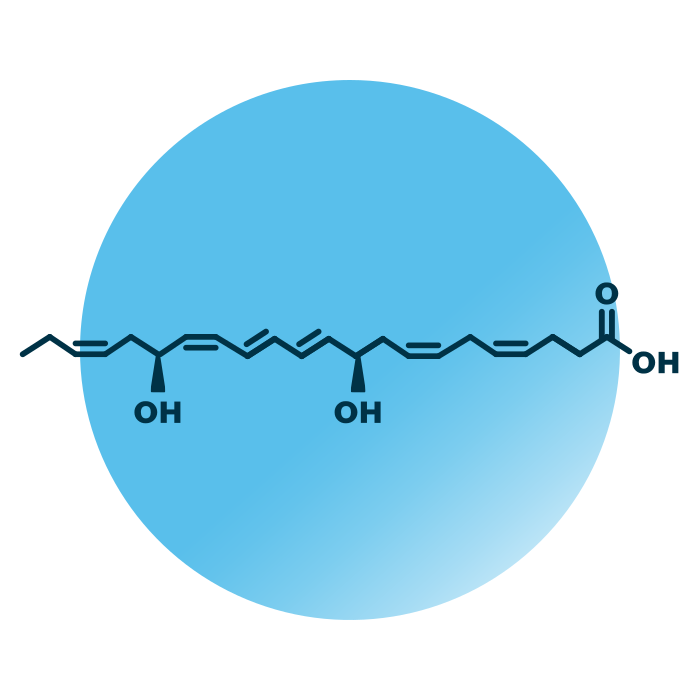
About the structure and biological function of PD
Structure. Protectins (PD) belong to the group of docosanoids within the fatty acyls. Their structure is based on docosanoic acid, a twenty-two carbon atoms long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group. The chain contains six double bonds of which three are in conjugation. The hydrocarbon chain of PDs can further feature oxygen containing substituents.
Function. Protectins are lipid mediators with significant inflammation-resolving and neuroprotective activities which they exert by interacting with specific G-protein-coupled receptors. They are part of the ‘Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators’ (SPMs), a small set of fatty acyl lipids which are intimately involved in the resolution of inflammation, and thus clearing the effects of pro-inflammatory fatty acyls, such as leukotrienes and prostaglandins.