About the structure and biological function of SCFA
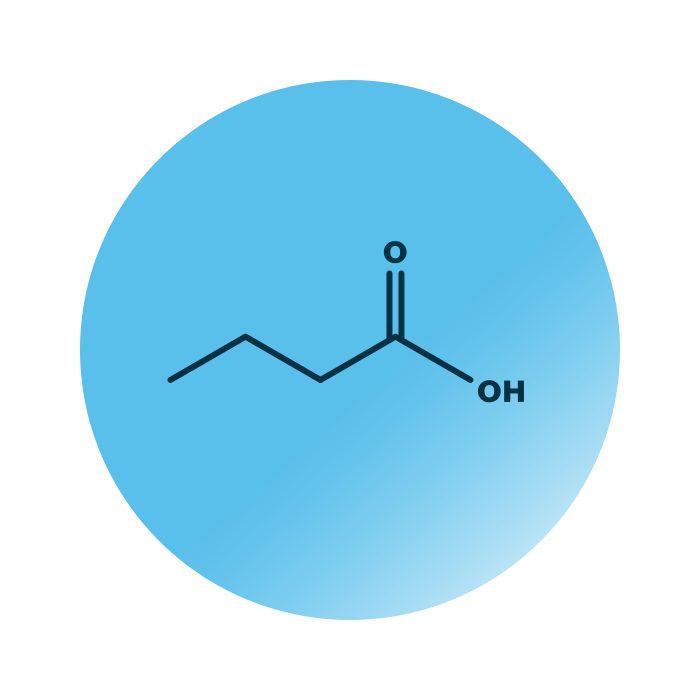
Structure. Short chain fatty acids (SCFA) belong to the group of fatty acids within the fatty acyls. Their structure consists of a hydrocarbon chain of five or less carbon atoms and a carboxylic head group. The hydrocarbon chain of SCFAs rarely contains double bonds, yet they can be branched or linear.
Function. Short chain fatty acids are biosynthetic precursors to further fatty acids, other lipids, and some amino acids. Yet, their biological function extends beyond that. Some SCFAs also play a role in signaling related to cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, programmed cell death. They are also important substrates for energy metabolism and can be found in milk fats. Further, some short chain fatty acids act as anti-inflammatory agents.