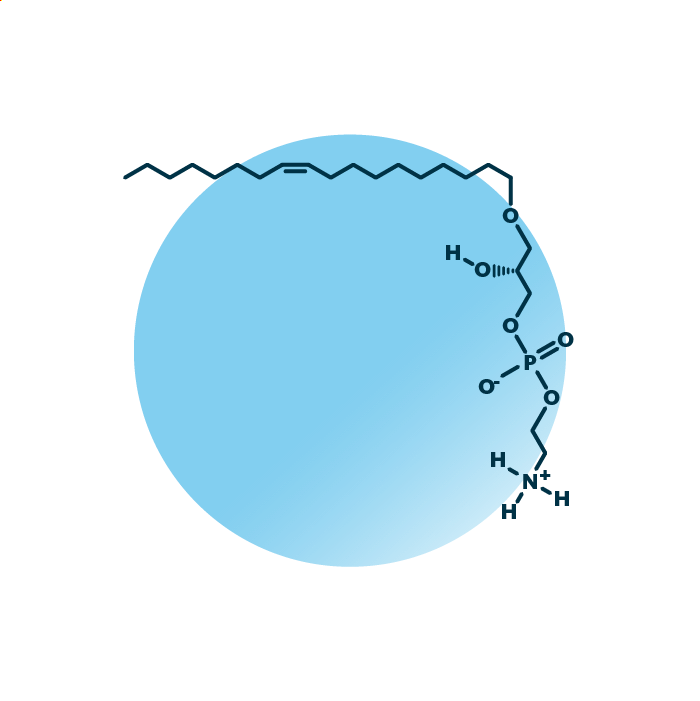
About the structure and biological function of LPE O-
Structure. Ether-linked lyso-phosphatidyl-ethanolamines (LPE O-) belong to the group of ether phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to a fatty alcohol via an ether bond and a phosphoethanolamine molecule. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Little is known about the biological function of ether-linked lyso-phosphatidyl-ethanolamines, but they are precursors to ether-linked phosphatidyl-ethanolamines. In the pigmented layer of the human retina that nourishes retinal visual cells, LPE O- lipids are linked to the formation of bisretinoids. Bisretinoids are a family of fluorescent molecules that form in photoreceptor cells and contribute to some retinal diseases, thus LPE O- lipids are suggested to play a role in retinal health.