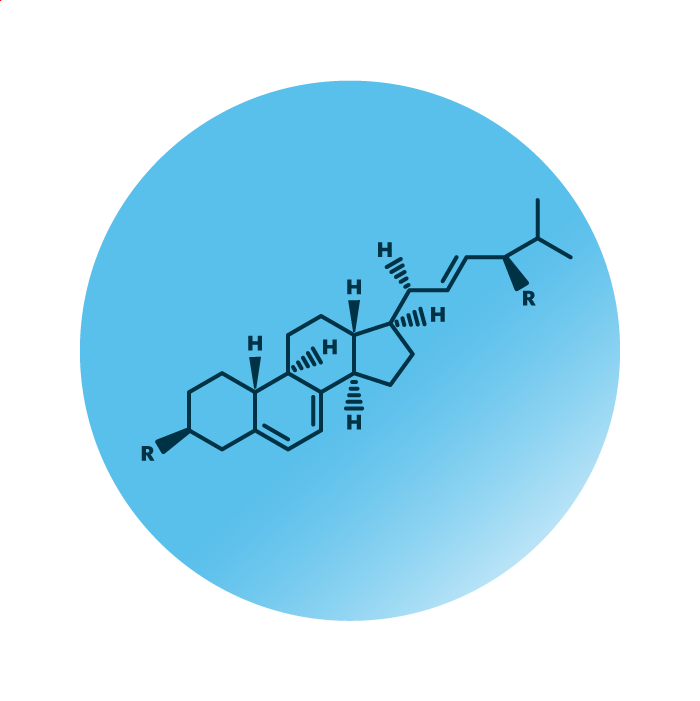
Structure. Ergosterol lipids belong to the sterol lipids. Their structure consists of the steroid structure, four linked hydrocarbon rings, to which a characteristic carbon side-chain is attached and two further methyl groups. Like in cholesterol lipids, the steroid structure, the side-chains, and the methyl groups of ergosterol lipids can be modified.
Function. Ergosterol lipids are present in plants and fungi. Like cholesterol, ergosterol serves an important structural role in the cell membrane and also forms lipid rafts. It also has multiple functions in growth regulation and is a precursor to vitamin D2.
Similar to cholesteryl esters, ergosteryl esters (EE) mainly serve as fungal pool for both of its components, ergosterol and the fatty acid. Further ergosterol lipids such as campesterol, brassicasterol or stigmasterol are often collectively coined as phytosterols. Like cholesterol lipids, phytosterols serve important functions in plant membranes and their esters function as storage and transportation forms.