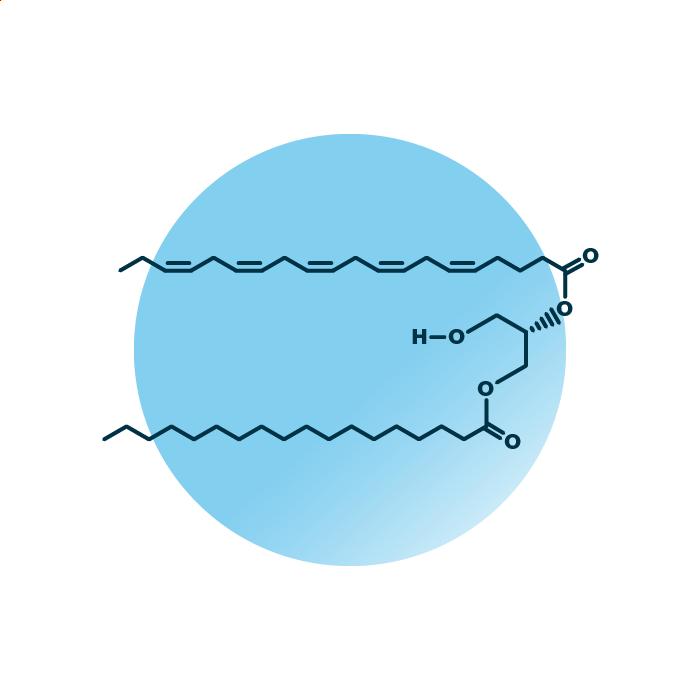
About the structure and biological function of DAG
Structure. Diacylglycerols (diglycerides, DAG, or DG) belong to the group of glycerol esters within the glycerolipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to two fatty acids. The fatty acids can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Diacylglycerols have different biological functions, of which many depend on the position of the two fatty acids at the glycerol backbone. Thus, diacylglycerols serve as key intermediates in the synthesis of phospholipids and glycerolipids such as triacylglycerols. They can also function in cellular signaling, and their physical properties influence cell membrane biophysics. They are important immunomodulators. Further, diacylglycerols accumulate in many organs in obesity and can be an important factor in cancer.