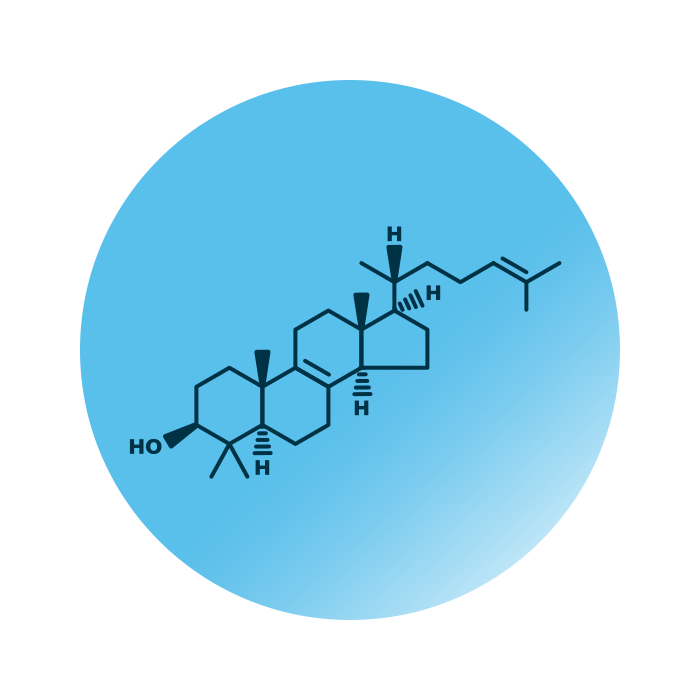
About the structure and biological function of Lano
Structure. Lanosterol (lanosta-8,24-dien-3β-ol, or Lano) belongs to the group of cholesterol lipids within the sterol lipids category. Its structure consists of four linked hydrocarbon rings, the steroid structure. A hydrocarbon tail containing a double bond is linked to one end of the steroid, a hydroxyl and two methyl groups are linked to the other end.
Function. Lanosterol is the first steroidal intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol in animals and of ergosterol in fungi. Lanosterol contributes to protein homeostasis by dissolving and suppressing the aggregation of misfolded proteins and protein aggregates. These features have potential therapeutic applications in cataracts and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. Further, statin treatment reduces lanosterol level, reflecting the medication-induced lowering of cholesterol synthesis.