About the structure and biological function of NH
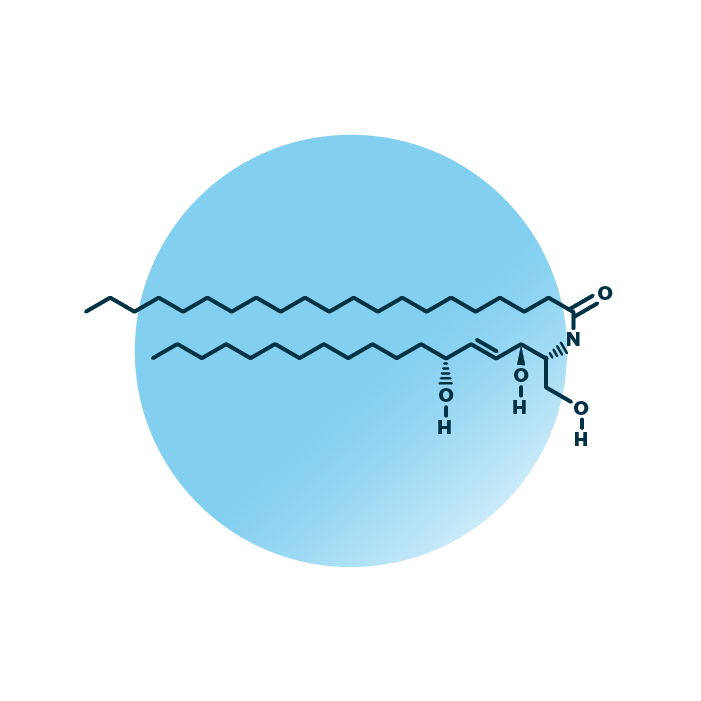
Structure. Non-hydroxy-fatty acid [N] 6-hydroxy-sphingosine [H] ceramides (CER[NH], or NH) belong to the group of ceramide lipids within the sphingolipids. Their structure consists of a sphingoid base, specifically 6-hydroxy-sphingosine, and a fatty acid, which is a non-hydroxy fatty acid. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. The biological role of non-hydroxy-6-hydroxy-sphingosines mainly revolves around skin health where they serve structural and signaling roles. NH ceramides contribute to epidermal barrier function which protects against environmental factors and prevents trans-epidermal water loss. Imbalanced skin ceramides can contribute or lead to the development of skin conditions. Further, NH ceramides are increased during winter months in healthy skin.