Cholesterol
Details
Lipid Category
Lipid Group
Lipid Class
About the structure and biological function of Chol
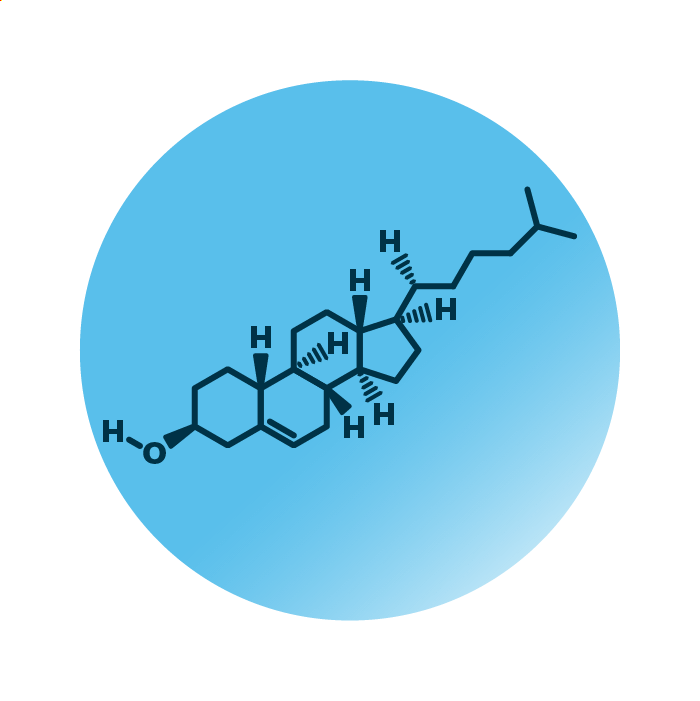
Structure. Cholesterol (Chol) belongs to the group of cholesterol lipids within the sterol lipids. Its structure consists of four linked hydrocarbon rings, the steroid structure. A hydrocarbon tail is linked to one end of the steroid, a hydroxyl group linked to the other end.
Function. Cholesterol has a vital function in animals. It is an essential component of cell membranes and lipid rafts. It is a precursor of steroid hormones and other metabolites such as vitamin D or bile acids. Cholesterol also is important for cell signaling, transport processes, and regulation of gene readout, and an abundant constituent of the water permeability barrier in skin and of myelin in the brain. Further, excess cholesterol is linked to cardiovascular disease.
Chol lipidomics analysis with
Lipotype
| Structural details | class level |
| Variants identified | 1 |
| Approach | untargeted/targeted |
| Method | mass spectrometry |
| Device | Q Exactive Orbitrap (280.000 Res) or Agilent 1290 HPLC + 6495 Triplequad |
| Quantification | yes |
| Delivery time | 2-6 weeks |
| Lipidomics data | pmol & mol% |
| Figures | included |
TAG, DAG, EOdS, EOS, EOP, EOH, NdS, NS, NP, NH, AdS, AS, AP, AH, Chol, CE
2Blood Basic includes:
TAG, DAG, PC, PE, PI, LPC, LPE, PC O-, PE O-, Cer, SM, Chol, CE
EXAMPLE STRUCTURE
Chol
Interested in
Chol
analysis?
★★★★★


