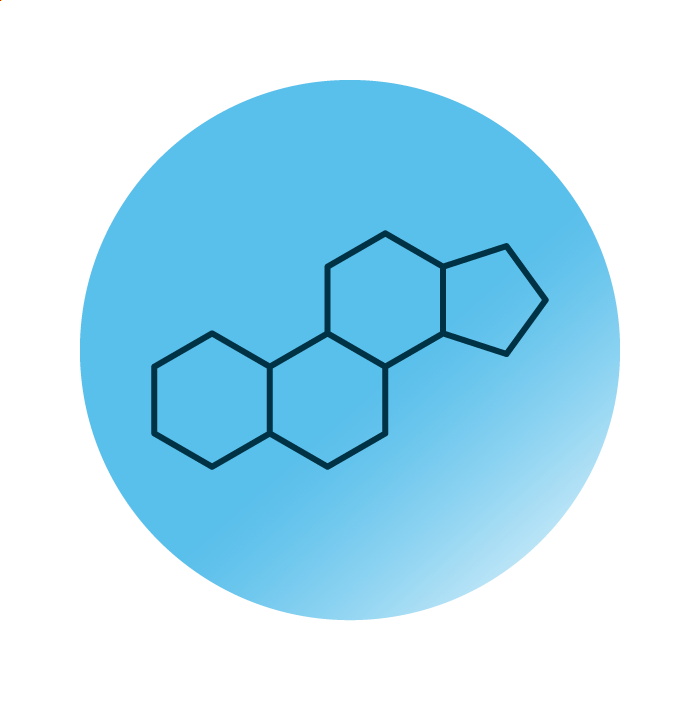
Structure. Sterol lipids are one of the eight categories of lipids and contain thousands of lipid species. All of these feature a similar molecular structure: they consist of the steroid structure, four linked hydrocarbon rings. Fatty acids, characteristic side-chains, functional groups, sugars, and double bonds – the steroid structure can be modified on hundreds of levels.
Function. Sterol lipids are found predominantly in eukaryotes but also in some prokaryotes. Great differences apply regarding the types of sterol lipids to be found in an organism. The most prominent sterol lipids are the cholesterol lipids which can be found in animals. They are precursors to steroid hormones, and important for cell signaling, transport processes, and regulation of gene readout, and esterified cholesterols serve also as storage for fatty acids.
Ergosterol lipids are the plant and fungi counterparts to cholesterol lipids. Steroids are a type of sterol lipids which encompass many sterol lipid-based hormones, and secosteroids contain the different classes of vitamin D which are important to bone formation. Bile acids are the end products of cholesterol lipids in animals and serve important functions in the digestion of fats.