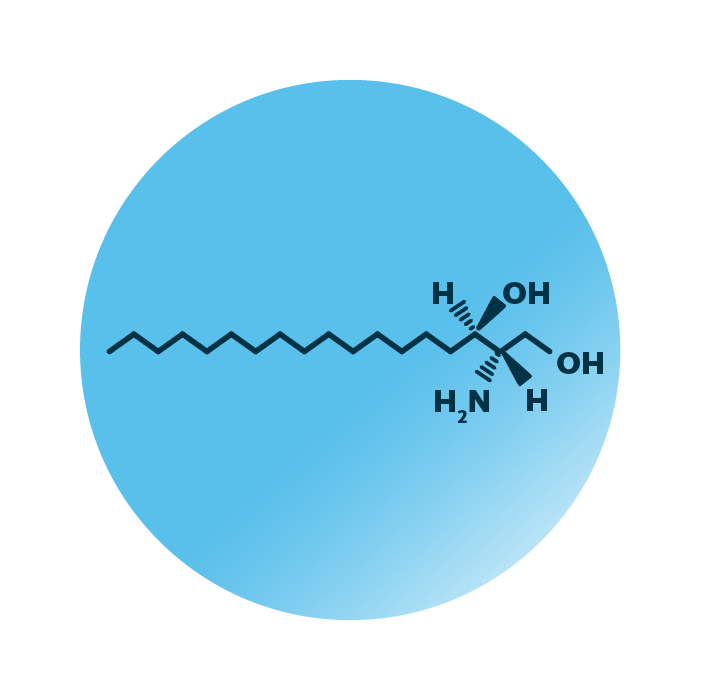
About the structure and biological function of dhSph
Structure. Sphinganines (dihydrosphingosines, D-erythro-sphinganines, or dhSph) belong to the group of sphingoid bases within the sphingolipids. Their structure consists of an amino alcohol with a saturated hydrocarbon chain.
Function. Sphinganines serve an important biological function as biosynthetic precursors to sphingosine and thus more complex sphingolipids. Little is known about the cell biological function of free sphinganines aside their difference from sphingosines. However, it has been linked to sleep apnea and sepsis. Additionally, some fungi produce sphinganine analog mycotoxins to disrupt sphingolipid metabolism in plants.