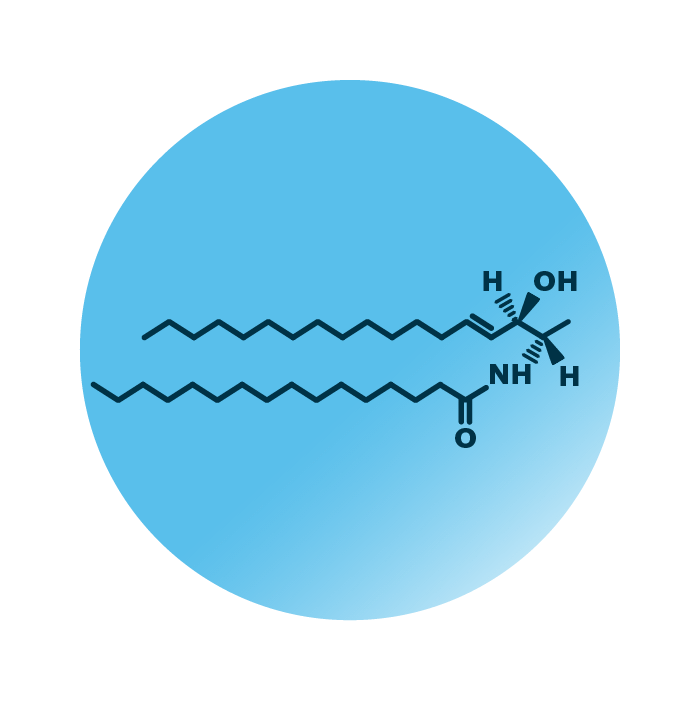
About the structure and biological function of doxCer
Structure. Deoxyceramides (deoxyCer, or doxCer) belong to the group of ceramide lipids within the sphingolipids. Their structure consists of a sphingoid base, specifically deoxysphingosine, and a fatty acid. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Deoxyceramides augment the presentation of small glycolipid antigens to T cells and have been linked to therapy-induced senescence, a state of cell cycle arrest in response to chemotherapy. High levels of deoxyCer have also been found in obese patients with type 2 diabetes and dietary interventions have been shown to affect these. Deoxyceramides are suggested to be potential biomarkers insulin sensitivity.