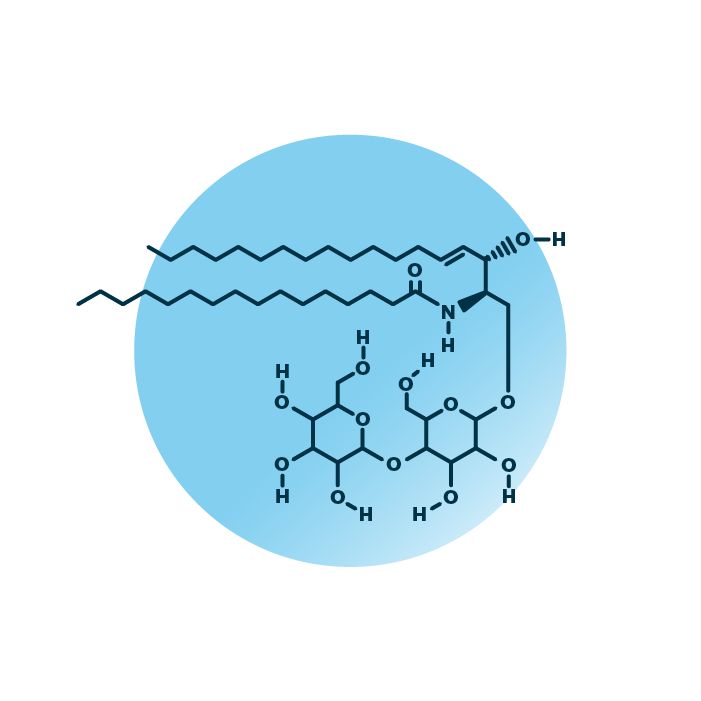
About the structure and biological function of DiHexCer
Structure. Dihexosylceramides (CerG2, or DiHexCer) belong to the group of diglycosylceramides within the sphingolipids. Their structure consists of a ceramide backbone linked to a neutral disaccharide molecule. The ceramide backbone contains two hydrocarbon chains: a long-chain base which is linked to a fatty acid via an amide bond. The fatty acid and the long-chain base can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Many dihexosylceramides are key intermediates in the biosynthesis of glycosphingolipids containing three or more sugar molecules such as globosides and gangliosides. Yet, they are vital to cell function and particularly important to lipid raft formation in cells of the innate immune system. They bind to pathogens, mediating immune and inflammatory responses. Further, dihexosylceramide metabolism aberrations are linked to cancers, cardiovascular disease, inflammation, and multiple sclerosis.