About the structure and biological function of NS
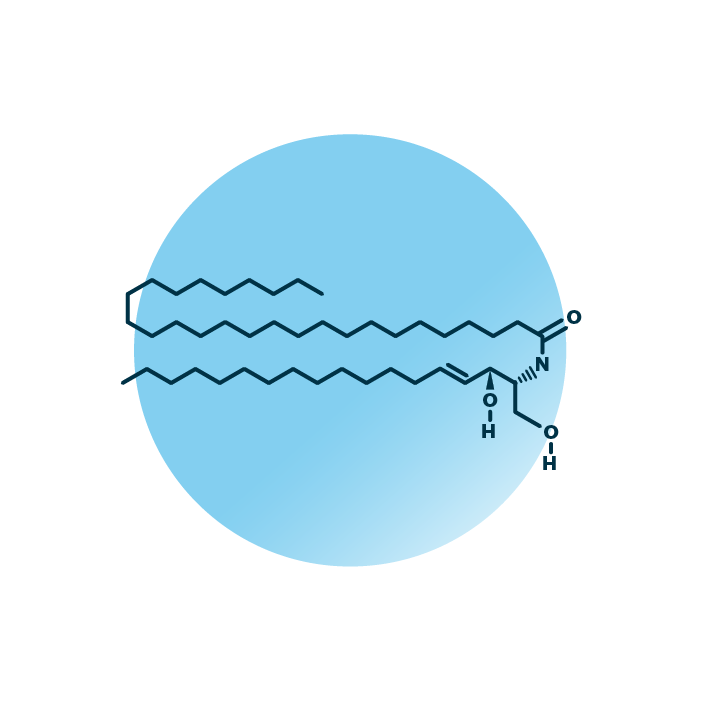
Structure. Non-hydroxy-fatty acid [N] sphingosine [S] ceramides (CER[NS], or NS) belong to the group of ceramide lipids within the sphingolipids. Their structure consists of a sphingoid base, specifically sphingosine, and a fatty acid, which is a non-hydroxy fatty acid. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Non-hydroxy-sphingosines are mainly associated with human skin where they fulfill structural and signaling purposes. NS ceramides contribute to epidermal barrier function to protect against the environment and prevent trans-epidermal water loss. Skin ceramide profile aberrations can lead or contribute to skin conditions. An increase of NS ceramides is associated with psoriasis, a decrease is linked to dry skin. Further, a Nordic diet decreases NS levels in liver but increases brain levels.