About the structure and biological function of Pgd
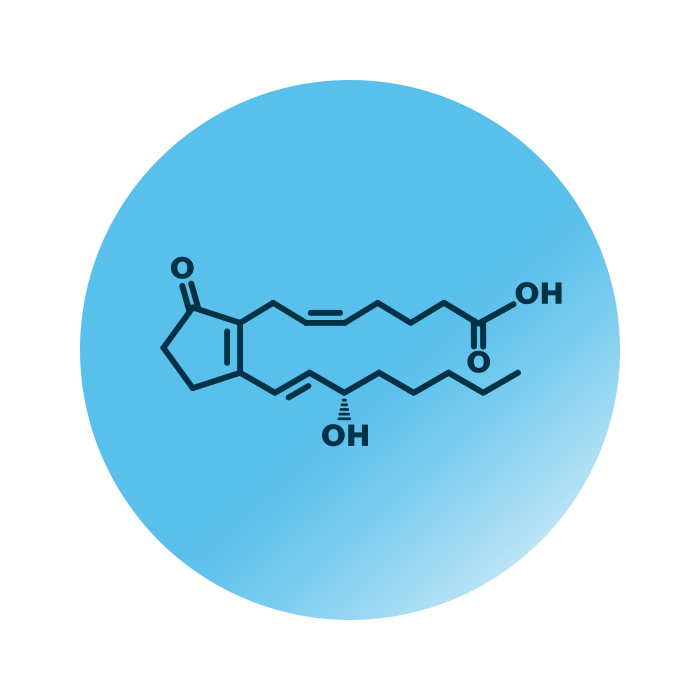
Structure. Prostaglandins (Pgd) belong to the group of eicosanoids within the fatty acyls. Their structure is based on eicosanoic acid, a twenty carbon atoms long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group. The chain contains one five-membered ring made of the carbon atoms eight to twelve. The substituents of the ring define the name of the Pgd species and all prostaglandins contain at least a hydroxyl group on carbon atom 15 and a double bond at carbon atom 13.
Function. Prostaglandins are associated with hormone-like functions. They interact with G-protein-linked receptors on the cell surface to activate cellular signal transduction pathways. Pgds coordinate a multitude of physiological processes, sometimes opposing depending on cell type and stimuli. The best-known function of Pgds in cells is that they modify inflammatory response. Prostaglandin synthesis is inhibited by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin to limit their pro-inflammatory effects.