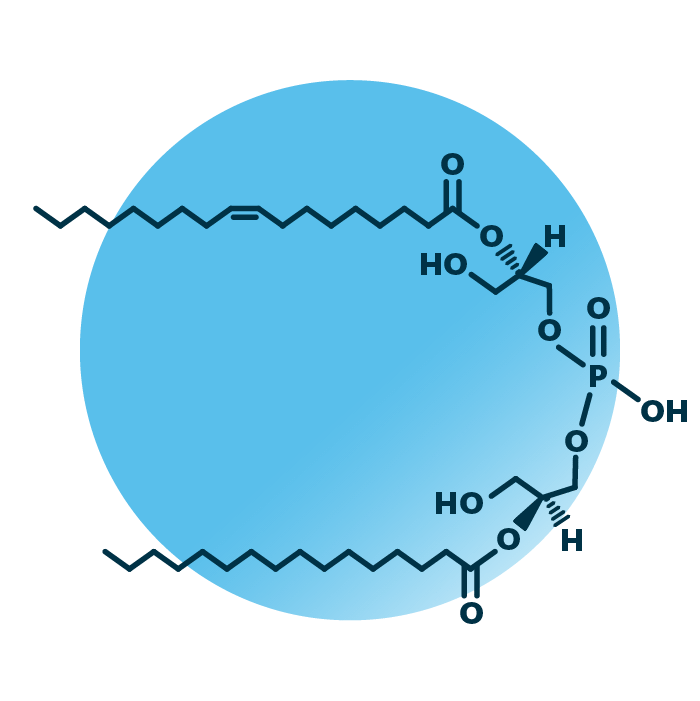
About the structure and biological function of BMP
Structure. Bis-(monoacylglycero)-phosphates (LBPA, or BMP) belong to the group of ester phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of two monoacylglycerols linked to each other via a phosphate. In total, BMPs contain two ester-linked fatty acids. They can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Bis-(monoacylglycero)-phosphates play diverse roles in cellular physiology and disease. They are markedly enriched in endosomal and lysosomal vesicles and are involved in membrane docking and digestion, and play a role in lysosomal storage diseases. BMPs are also researched as a non-invasive biomarker to monitor phospholipidosis with drug-induced toxicities. Further, BMPs have been identified as an important actor in the host endocytic machinery hijacked by certain viruses.