About the structure and biological function of PS
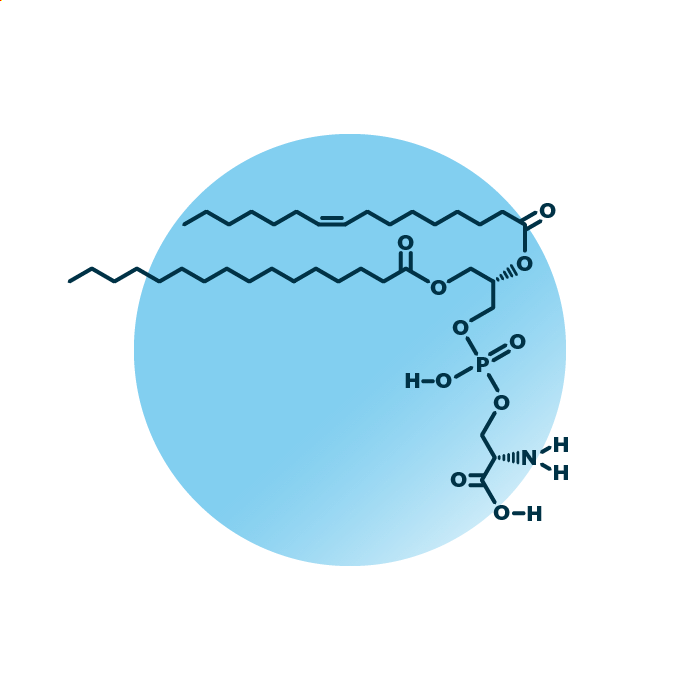
Structure. Phosphatidyl-serines (PtdSer, GPSer, or PS) belong to the group of ester phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to two fatty acids and a phosphoserine molecule. The fatty acids can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Phosphatidyl-serines are essential membrane components and contribute to the organization of protein complexes on the cytosolic side of the membrane, thus facilitating signaling activities. They also serve as precursors for lyso-phosphatidylserines, and for phosphatidylethanolamines. They are essential cofactors that bind to and activate many proteins with signaling functions. Further, phosphatidylserines are an important element of the blood coagulation process in platelets, and have a role in regulation of apoptosis, programmed cell death.