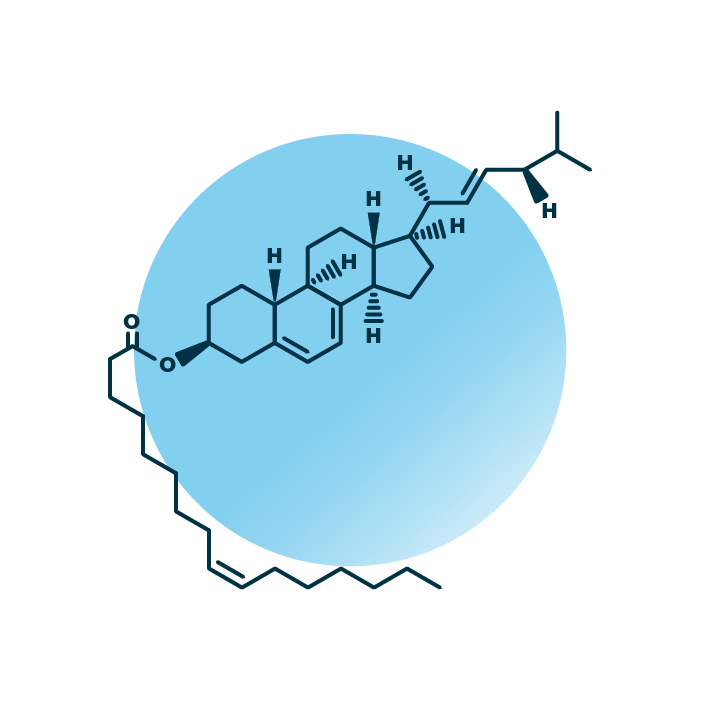
About the structure and biological function of EE
Structure. Ergosteryl esters (ergosterol esters, or EE) belong to the group of ergosterol lipids within the sterol lipids. Their structure consists of ergosterol where an ester bond is formed between the hydroxyl group of the steroid structure and a fatty acid. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. The biological function of ergosteryl esters revolves mainly around ergosterol storage in yeast. During growth retarding conditions but also after fungal death, ergosterol is esterified and stored in cellular lipid droplets. Once esterified, the fatty acids of the ergosteryl esters are not scavenged even during starvation conditions. Further, some ergosteryl esters also show strong growth inhibitory activity against dairy and cosmetic spoilage bacteria.