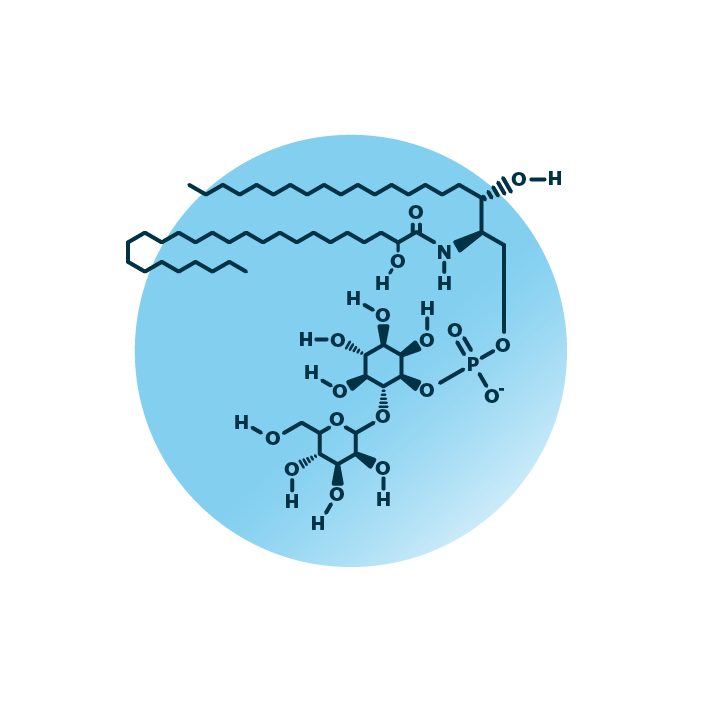
About the structure and biological function of MIPC
Structure. Mannosyl-inositolphosphoryl-ceramides (mannose-inositol-P-ceramides, or MIPC) belong to the group of phosphosphingolipids within the sphingolipids. Their structure consists of a ceramide backbone bound to a mannosylated phosphorylinositol molecule. The ceramide backbone contains two hydrocarbon chains: a long-chain base which is linked to a fatty acid via an amide bond. The fatty acid and the long-chain base can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Mannosyl-inositolphosphoryl-ceramides are important components of biological membranes of fungi. Together with M(IP)2C, they constitute the major sphingolipids in yeasts, where they have multiple functions related to maintenance of cell morphology and are required for the localization of cell membrane proteins. Depending on the immune status of the host, MIPC ceramides of the pathogenic yeast candida albicans indirectly cause immune system disorder and persistent fungal disease.