About the structure and biological function of LPC
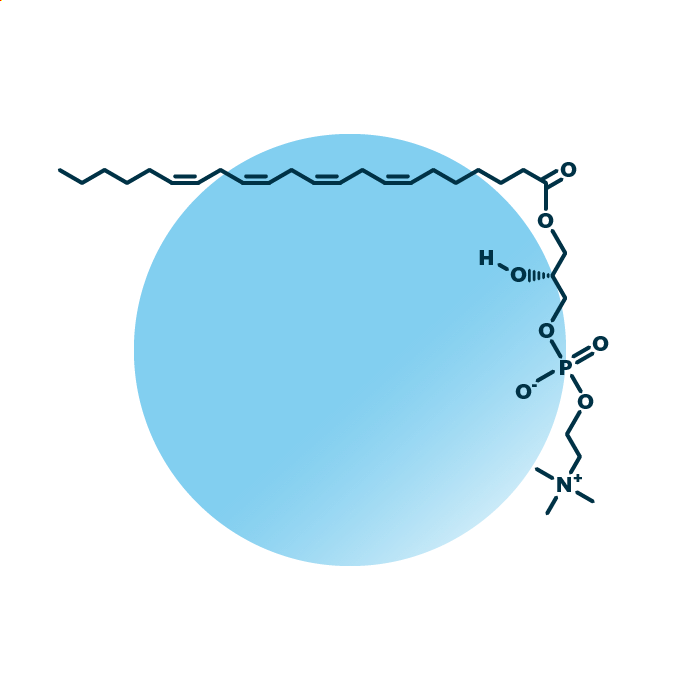
Structure. Lyso-phosphatidyl-cholines (lysolecithin, LysoPtdCho, LysoPC, or LPC) belong to the group of ester phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to a fatty acid and a phosphocholine molecule. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Lyso-phosphatidyl-cholines are potent signaling molecules and they have many functions related to inflammation and the immune system. They are suggested an important factor for neurodegeneration such as cognitive decline and dementia, and promote demyelination of neurons. Impaired levels of LPCs are also linked to cardiovascular disease and cancers. They have some functions in cell signaling. Further, LPC lipids have beneficial effects by activating macrophages.