About the structure and biological function of LPG
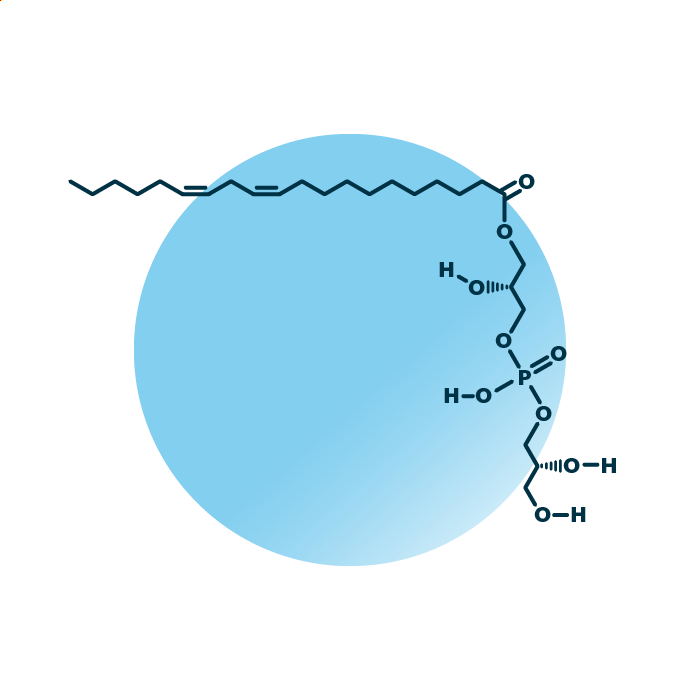
Structure. Lyso-phosphatidyl-glycerols (LysoPtdGro, LysoPG, or LPG) belong to the group of ester phospholipids within the phospholipids. Their structure consists of a glycerol backbone linked to a fatty acid and a phosphoglycerol molecule. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. Little is known about the function of lyso-phosphatidyl-glycerols in animals. Elevated LPG levels have been detected in acute coronary syndrome and they may be linked to cardiovascular diseases. In bacteria, LPGs are the lipid backbone elements of lipopolysaccharides, structural components of the bacterial capsule which are important virulence factors for many pathogens. Further, LPG lipids serve as precursors for phosphatidylglycerols.