About the structure and biological function of EOS
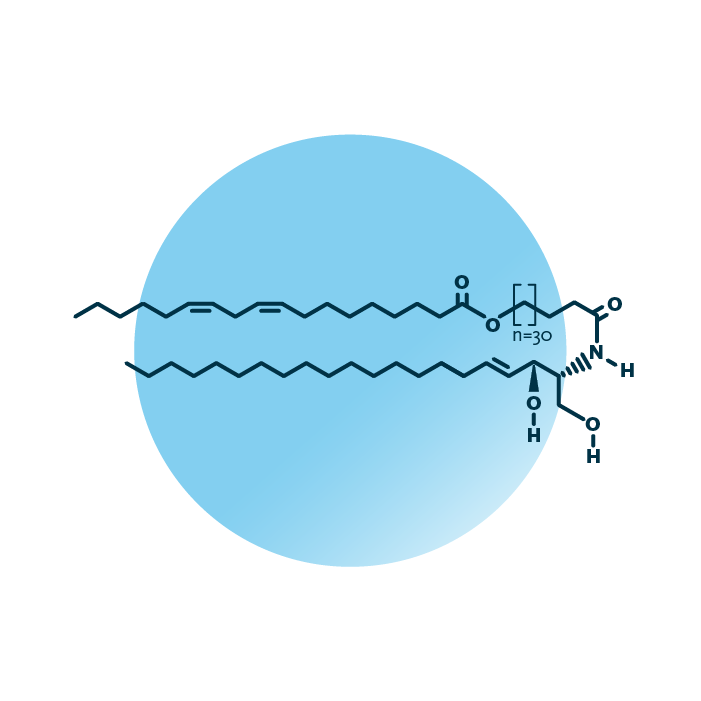
Structure. Omega-hydroxy-fatty acid [EO] sphingosine [S] ceramides (CER[EOS], or EOS) belong to the group of ceramide lipids within the sphingolipids. Their structure consists of a sphingoid base, specifically sphingosine, and a fatty acid. The fatty acid is an ω-hydroxy fatty acid and “elongated” by a further fatty acid via an ester bond. The fatty acid can be of variable length, hydroxylated, and contain double bonds.
Function. The biological function of omega-hydroxy-sphingosines is tightly linked to skin health where they serve mainly structural roles. EOS ceramides are important to the lamellar phase of the epidermal barrier function which prevents trans-epidermal water loss but also protects against environmental factors. Skin ceramide imbalances can lead or contribute to the development of skin conditions. Decreased EOS levels are associated with atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and dry skin.